Memory Process
1. Encoding: the processing of information into the memory system
2. Storage: the retention of encoding material over time
3. Retrieval: the process of getting the information out of the memory stage
Recall v. Recognition
Recall: you must retrieve the information from your memory (aka fill in the blank tests)Recognition: you must identify the target from possible targets
Flashbulb Memory: a clear movement of an emotionally significant moment or event.
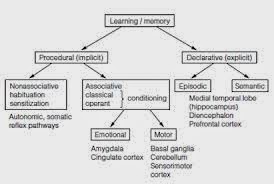
3 Types of Memory
1. Sensory Memory: based upon your senses
- the immediate initial recording of sensory information in the memory system
- stored just for an instant, and most gets unprocessed.
- 7 digits (+/- 2)
- the into will be stored into a long term or forgotten
Working memory has 3 parts:
- Audio
- Visual
- Integration of audio and visual (controls where your attention lies)
2 Ways to Encode
1. Automatic Processing - (involuntary) - unconscious encoding of incidental information.
- You encode space, time, and word meaning without effort.
- Things can become automatic with practice
- Rehearsal is the most common effortful processing technique.
- Through enough rehearsal, what was effortful becomes automatic.
Spacing Effect- we encode better when we study or practice over time
Serial Positioning Effect- our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list
Types of Encoding
1. Semantic Encoding- the encoding of meaning, like meaning of the words2. Acoustic Encoding- the encoding of sound, especially the sounds of words.
3. Visual Encoding- the encoding of picture images
Mnemonic Devices use imagery.
- often will occur automatically
2 Types of Retrieval Failure
Protractive Interference- the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new informationRetroactive Interference- the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
-Repression is apart of why people forget thingsMisinformation Effect- incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event



No comments:
Post a Comment